Chronic tonsillitis can last longer than two weeks.
Tonsillitis is an inflammation of the tonsils, and there are three types. Acute tonsillitis describes an infection that lasts three to 14 days. A patient has recurrent tonsillitis if they have multiple bouts of tonsillitis in a single year. Chronic tonsillitis is tonsillitis that lasts longer than 14 days.
Causes
While tonsillitis is usually considered an illness that affects children, chronic tonsillitis is actually more common in teenagers and adults. It is usually caused by a bacterial infection, but it can be caused by a viral infection.
Exposure to radiation can increase the risk of developing chronic tonsillitis.
Symptoms
Tonsillitis symptoms can vary depending on whether it is caused by a virus or a bacterium. Viral tonsillitis is often accompanied by symptoms resembling those of a cold like nasal congestion or coughing. Viral tonsillitis usually goes away on its own within two weeks.
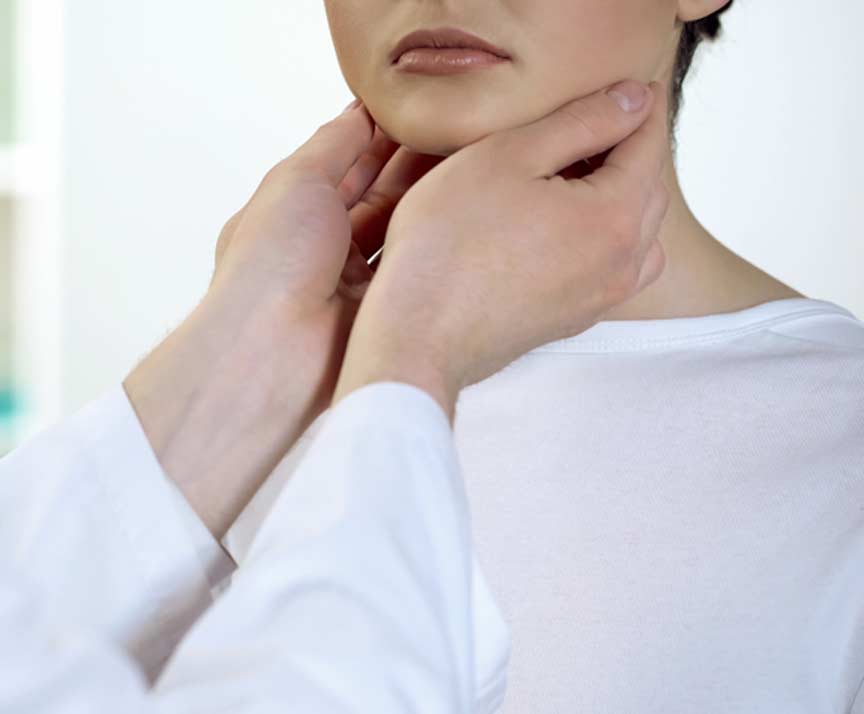
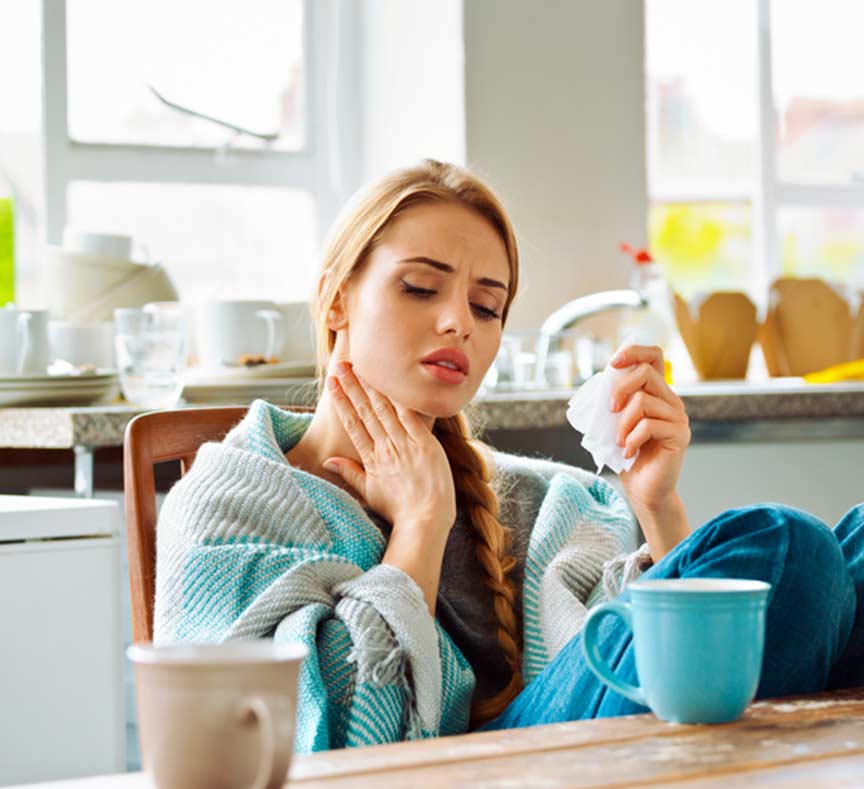


Bacterial tonsillitis, which is more likely to become chronic, is most often caused by group A beta-hemolytic streptococcus or GABHS. Patients with bacterial tonsillitis often have a sudden fever along with a sore throat. This type of tonsillitis is also often called strep throat.
Symptoms of chronic tonsillitis include a sore throat, swollen tonsils, enlarged lymph glands in the neck, and bad breath.
Patients with chronic tonsillitis may develop small crypts or pockets on their tonsils where bacteria can accumulate. The crypts also often contain tonsil stones or tonsilloliths, which are accumulations of debris on the tonsils. Tonsil stones have a foul smell and can cause a feeling of something being stuck in the back of the throat.
Sleep apnea is one possible complication of chronic tonsillitis. As the tonsils swell, they may block the airway and thus impair the patient’s ability to breathe while sleeping.
Chronic bacterial tonsillitis can also rheumatic fever – which can severely affect the valves of the heart. Other possible complications include skin rashes, pneumonia, sinusitis, and a kidney disorder called glomerulonephritis.
Treatment
The doctor will start with treatments designed to reduce pain and ensure that the patient remains well-hydrated. They will often recommend over-the-counter medications like ibuprofen, Tylenol, throat sprays, or lozenges.
The doctor may also prescribe antibiotics if the patient has bacterial tonsillitis.
If such conservative treatments don’t work, or the patient develops serious complications like sleep apnea, the doctor will recommend a tonsillectomy or surgical removal of the tonsils. The doctor will also recommend a tonsillectomy if the patient develops tonsil stones.
A specialist at Nasal & Sinus Surgery Center will perform the tonsillectomy, which is usually an outpatient procedure. The doctor may keep the patient overnight, however, if they are a young child or develop complications. They will administer general anesthesia so the patient will sleep through the procedure.
Most children need 10 to 14 days to recover from a tonsillectomy, and adults often take somewhat longer to recover. The patient should rest in bed for several days after the procedure, and they should drink plenty of fluids. They should eat foods that are soft and easy to swallow during recovery. The patient will be able to resume their normal schedule once they stop needing pain medication, can sleep through the night, and have returned to a normal diet.
